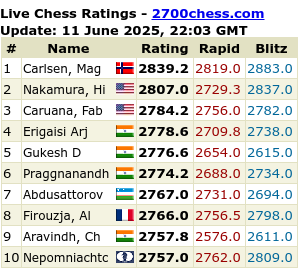
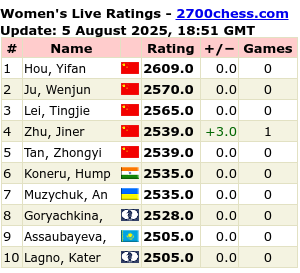
Tomorrow is….again…that time of year some of us don’t like at all….because all dogs want to hide in places you don’t have in your home, some dogs get lost due to some fireworks – which sound more like bombs and dog owners want to go mad at those setting of the fireworks (bombs) unexpectedly. Sometimes it goes non-stop during the night! We had some fireworks about 5 houses away from us Saturday night…maybe it was still some people celebrating Diwali…but it’s crazy! at about 1am/2am in the morning! I mean, some people are night owls, others not. It’s not to say that if you go to bed at 3am that you don’t have to respect your neighbours or people near you.
Image: supercoolpets.com
The Gunpowder Treason and Plot,
I know of no reason
Why Gunpowder Treason
Should ever be forgot.
The Museum of London is holding a Guy Fawkes study day on November 5, whilst over at the Museum in Docklands, Toy Theatre retells the story of Fawkes – but with a different ending. © London Museums
Please follow THIS LINK -which will open in a new window-to find out more!
Basically, Guy Fawkes was a man who tried to blow up the King of England by setting the Houses of Parliament ablaze in 1605. He was a member of an English Roman Catholic group who opposed the Protestant rule in England. English folks make effigies or stuffed figures representing the famous conspirator and burn them.
Image:britannica.com
On the 5th of November, the king and his leaders were about to meet. So, Guy Fawkes men placed barrels of gunpowder in one of the cellars beneath the building where the king was having his meeting. Guy Fawkes was to light the fuse that would set off the explosion. But the plot was discovered before he had a chance to do this. The king was saved, and Guy Fawkes was hanged
Ever since, Guy Fawkes Day has been a time for merrymaking. It is a holiday that both children and adults can enjoy. And the fun really begins when darkness falls, then “the “Guy” is tossed onto the bonfire, and set alight. Then the fireworks go off, and “the Guy” goes up in a flames.
As early as 1607 there are records of bonfire celebrations on the 5th of November. James I had declared the day a public holiday in his joy at the overthrow of the Gunpowder Plot.
Children would often blacken their faces with the ashes on Bonfire night, in imitation of Guy fawkes who it was believed to have done this also, to try to camouflage himself.
Guy Fawkes (13 April 1570 – 31 January 1606) sometimes known as Guido Fawkes, was a member of a group of English Roman Catholic revolutionaries who planned to carry out the Gunpowder Plot.
Although Robert Catesby was the lead figure in thinking up the actual plot, Fawkes was put in charge of executing the plan for his military and explosives experience. The plot was foiled shortly before its intended completion, as Fawkes was captured while guarding the gunpowder. Suspicion was aroused by his wearing of a coat, boots and spurs, as if he intended to leave very quickly.
Fawkes has left a lasting mark on history and popular culture. Held in the United Kingdom (and some parts of the Commonwealth) on November 5 is Bonfire Night, centred on the plot and Fawkes. He has been mentioned in popular film, literature and music by people such as Charles Dickens and John Lennon. There are geographical locations named after Fawkes, such as Isla Guy Fawkes in the Galápagos Islands and Guy Fawkes River in Australia.
The plot itself may have been occasioned by the realisation by Protestant authorities and Catholic recusants that the Kingdom of Spain was in far too much debt and fighting too many wars to assist Catholics in Britain. Any possibility of toleration by Great Britain was removed at the Hampton Court conference in 1604 when King James I attacked both extreme Puritans and Catholics. The plotters realised that no outside help would be forthcoming unless they took action themselves. Fawkes and the other conspirators rented a cellar beneath the House of Lords having first tried to dig a tunnel under the building. This would have proved difficult, because they would have had to dispose of the dirt and debris. (No evidence of this tunnel has ever been found). By March 1605, they had hidden 1800 pounds (36 barrels, or 800 kg) of gunpowder in the cellar. The plotters also intended to abduct Princess Elizabeth (later Elizabeth of Bohemia, the “Winter Queen”). A few of the conspirators were concerned, however, about fellow Catholics who would have been present at Parliament during the opening. One of the conspirators wrote a warning letter to Lord Monteagle, who received it on 26 October. The conspirators became aware of the letter the following day, but they resolved to continue the plot after Fawkes had confirmed that nothing had been touched in the cellar.
Lord Monteagle had been made suspicious, however; the letter was sent to the Secretary of State, who initiated a search of the vaults beneath the House of Lords in the early morning of 5 November. However, nothing was moved, in order not to alert the conspirators that the plot had been uncovered. Fawkes, who was resolved to blow himself up along with Parliament if need be, was seized as he attempted to ignite the powder charge. Peter Heywood, a resident of Heywood, Lancashire, snatched the torch from his hand at the last instant. Fawkes was arrested and taken before the privy council where he remained defiant. When asked by one of the Scottish lords what he had intended to do with so much gunpowder, Fawkes answered him, “To blow you Scotch beggars back to your own native mountains!”
When they asked for his name Fawkes replied “John Johnson”. He was tortured over the next few days. King James directed that the torture be light at first, but more severe if necessary. Sir William Waad, Lieutenant of the Tower of London at this time, supervised the torture and obtained Fawkes’s confession. For three or four days Fawkes said nothing, nor divulged the names of his co-conspirators. Only when he found out that they had proclaimed themselves by appearing in arms did he succumb. The torture only revealed the names of those conspirators who were already dead or whose names were known to the authorities. Some had fled to Dunchurch, Warwickshire, where they were killed or captured. On 31 January, Fawkes and a number of others implicated in the conspiracy were tried in Westminster Hall. After being found guilty, they were taken to Old Palace Yard in Westminster and St Paul’s Yard, where they were hanged, drawn and quartered.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guy_Fawkes. The link will open in a new window.

Image: britian4kiwikids.org.nz