Heart surgeon Dr. Christiaan Barnard illustrates a point while addressing a group of journalists in Cape Town, South Africa, on Dec. 10, 1967, a week after performing the first successful heart transplant operation in a human. Barnard’s patient, Louis Washkansky, died of pneumonia 18 days after the operation, but within weeks, other doctors began to perform similar surgeries.
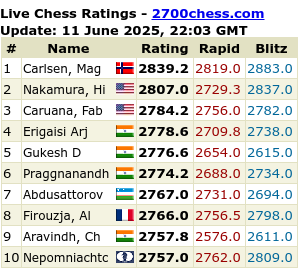
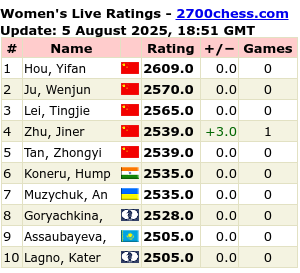
Dr Barnard: “For a dying person, a transplant is not a difficult decision. If a lion chases you to a river filled with crocodiles, you will leap into the water convinced you have a chance to swim to the other side. But you would never accept such odds if there were no lion.”
The first patient, 24-year-old Denise Darvall, had suffered severe head injuries earlier that day when she was struck by a car as she walked to a bakery to buy a cake. A neurosurgeon declared her brain-dead, and her father gave permission for doctors to harvest her heart. Barnard’s team draped the woman, sterilized her chest, and confirmed that their heart-lung machine, which keeps cells alive, was operational.
Midnight passed, and now it was Dec. 3, 1967.
Barnard’s assistants opened Darvall, connected her heart to the machine, and began to cool her body. When it had reached the proper temperature, they excised Darvall’s heart and placed it in a bowl of ice-cold solution. Unlike the woman’s brain, the heart was perfectly healthy.
Barnard was in an adjacent operating room with the second patient, 55-year-old businessman Louis Washkansky, who had been anesthetized after signing a consent form that essentially rendered him a guinea pig. Washkansky suffered from debilitating coronary disease for which there was no cure. Without a transplant, he would soon die.
Although an American doctor in 1964 had sewn a chimpanzee’s heart into a person who lived but a few hours, no one had ever tried to transplant a human heart — but several surgeons, including Barnard, had experimented with transplanting a heart from one dog to another. By December 1967, Barnard, 45, was ready to leave the lab.
Barnard opened Washkansky, connected him to a separate heart-lung machine, and quickly cut out his damaged organ, replacing it with the young woman’s. Then he tested the sutures. They held strong. Washkansky’s new heart had stopped beating, but the cold had sustained it and one shock of electricity restarted it. Barnard slowly weaned his patient off the heart-lung machine. At 8:30 a.m., Washkansky was wheeled out of the operating room. The beat of his new heart was strong.
Word of the operation had been leaked to reporters, who awaited its outcome at the hospital. One doctor told the Associated Press that jolting Washkansky’s new heart back into action “was like turning the ignition switch of a car.” Barnard told another wire service that Washkansky deserved the credit. “If it had not been for this man’s courage and will to live,” he said, “the operation would never have succeeded.”
Reports of the operation made headlines around the world, including front-page stories Dec. 4 in The New York Times and The Providence Journal. Pneumonia would kill Washkansky 18 days after his transplant, but a new era had arrived.
Forty years later, untold thousands of people who would have been in their graves now are leading normal lives.
Jim Taricani, who received a new heart in 1996 after years of progressive heart failure, is one of them.
This did not seem his future when Taricani, 58, now an investigative reporter for Channel 10, was a young man. He smoked and had high blood pressure, but there were no other clues into what fate held for him. He exercised regularly and had never experienced any of the typical symptoms of heart disease: angina, shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness. To his knowledge, only one relative had a history of cardiac disease: his maternal grandmother, who died at the age of 78 during her fifth heart attack.
At 3:06 a.m. on July 9, 1986, pain that he would later compare to an elephant on his chest awakened Taricani. He thought he’d pulled a muscle the day before while lifting weights at his gym, and he left his bedroom for the kitchen, where he hoped stretching would soothe him. It did not. The pain intensified and spread to his left arm, not a promising sign. He woke his wife, Laurie.
“I think you’d better take me to the hospital,” he said.
I’m going to die, Taricani thought to himself. I’m only 36, and I’m going to die.
“You’re in the middle of a major heart attack,” an emergency room doctor said when Taricani arrived at South County Hospital. A blood clot in an artery to his heart had stopped the flow of blood, killing substantial tissue. But the doctors saved Taricani, and he was transported to Rhode Island Hospital, where he stayed for 16 days. A few weeks later, he returned to work — and, he hoped, an ordinary life.
In February 1987, he suffered a second heart attack.
Cardiologists at Providence’s Miriam Hospital took charge of his care, prescribing drugs and admitting him when his heart lost normal rhythm, as it did repeatedly. As the 1980s ended, Taricani was becoming short of breath. His energy flagged and his abdomen bloated as his kidneys deteriorated. He’d entered an early stage of dying.
In November 1993, Laurie returned home to find her husband collapsed on the floor. When an ambulance delivered him to Miriam Hospital, his cardiologist, Dr. Richard Shulman, said: “You need a defibrillator and you’re going to need a heart transplant someday.” Heart transplants are not performed in Rhode Island and Shulman referred Taricani to Boston’s Massachusetts General Hospital, where doctors implanted a defibrillator, a device that would automatically shock his heart back into normal beating with a jolt of electricity when it lost rhythm. A transplant was inevitable now.
Taricani was 44 years old, and scared.
Oh my God, he thought, a heart transplant. Somebody’s going to cut my heart out — they’ve got to get a donor. Why me?
BARNARD INTENDED to be a general surgeon when he enrolled in a training program at the University of Minnesota in the mid-1950s. But working with the university’s open-heart pioneer, Dr. C. Walton Lillehei, headed him in another direction. He returned to his native South Africa, where he specialized in heart surgery — and briefly attracted attention, in 1960, when he transplanted a second head onto a dog. Barnard was a technically flawless surgeon, though no prominent innovator. But he had an ego.
On a visit to the United States early in 1967, Barnard became familiar with the experimental work of Dr. Norman Shumway, another surgeon trained in Minnesota who was a professor at California’s Stanford University School of Medicine. Shumway had devised an ingenious heart transplant operation — with dogs. He planned eventually to move to humans.
Using Shumway’s methods, Barnard beat him — unfairly so, many said. Shumway might have accomplished the first human heart transplant if his superiors had not thought he was restricted by California ethics laws — ones that did not apply in South Africa — regarding the definition of death.
Barnard’s transplant operation on Dec. 3, 1967, inspired his colleagues worldwide. Just three days later, a New York City surgeon cut a heart from a baby born without a brain and sewed it into a heart-crippled infant who died hours later. Barnard performed his second transplant on Jan. 2, 1968. Four days later, when Stanford’s administrators lifted their restriction, Shumway performed his first.
By the end of 1968, surgeons in Bombay, Paris, London and elsewhere were transplanting hearts. Barnard had become an international sensation.
WHENEVER HIS implanted defibrillator went off, the shock would kick Taricani halfway across a room. It went off only a few times in 1994 and 1995, but more frequently as 1996 progressed.
He was shaving on the morning of July 19, 1996, when his heart lost rhythm once more, activating the defibrillator and knocking him to the floor. He stood, and the defibrillator fired again. He crawled out of the bathroom, and the machine went off a third time, flipping him onto his back. He was turning blue.
Read more on this link…
Photo and article of Dr Barnard here. The Link will open in a new window.
“He was one of our main achievers, a pioneer in heart transplant” ++++++Nelson Mandela
” We owe him a great debt of gratitude ” +++++Mikhail Gorbachev
JOHANNESBURG (AFP) – Forty years ago, in the middle of the night at a Cape Town hospital, South African surgeon Christiaan Barnard rewrote medical history when he carried out the first ever heart transplant.
The operation captivated the imagination of the world, catapulting Barnard and South Africa onto the world stage and leading to hundreds of similar operations around the globe.
Dene Friedman, who was in the theatre during the groundbreaking operation, assisting with the running of the heart-lung machine, remembers the surgery “as if it were yesterday”.
“Nobody took a photograph, nobody did anything … We didn’t think of the publicity side of it,” she told AFP.
Barnard had not even told the hospital that he would be attempting the operation, giving little thought to the reaction his techniques would generate.
“Professor Barnard told them in the early hours of the next morning. He just gave a phone call,” remembers Friedman.
“We just thought that we were doing something worthwhile for the patient,” she said of Louis Washkansky, a 53-year-old diabetic with incurable heart disease who had suffered three heart attacks.
Barnard had already practised the basic surgical technique for the transplant — that was pioneered by other surgeons on animals — in the laboratory. He only needed one donor to put this knowledge into practice.
On the night of the December 2, 1967, a 25-year-old woman was fatally injured in a car accident.
Her blood type matched that of Washkansky’s and her father agreed that her heart could be donated for the surgery.
“We entered the theatre in the middle of the night and left at 8 am the next morning,” said Friedman.
“It was very impressive, exciting and scary. As it had never been done before, we weren’t sure about the effects in a human patient.”
The 30-strong medical team looked on in rapture as the transplanted heart gave its first few beats, making medical history.
Read here more about Dr Chris Barnard.
Another link about Dr Chris Barnard and his transplant.
image: gis.deat.gov.za